Interface
State Charge
When silicon dioxide is forming
on the single-crystal silicon surface, there is an abrupt change at the
silicon-silicon dioxide interface. There are always some dangling bonds at the
silicon-silicon dioxide interface because of the crystal structure mismatch.
The dangling bonds induce
so-called interface state charge, which is a positive charge that strongly
affects IC chip performance and reliability.
During IC chip manufacture
hydrogen or some other atoms can diffuse to the silicon-silicon dioxide
interface and attach to the dangling bonds resulting in changes in the
interface state charge and this in turn changes the threshold voltage (VT)
of the MOS transistors and finally the performance of the IC device.
Introducing HCl in the oxidation
helps to minimize the number of dangling bonds as some of the chlorine atoms
can be integrated into the silicon dioxide film and bind with silicon at the
Si-SiO2 interface.[3]
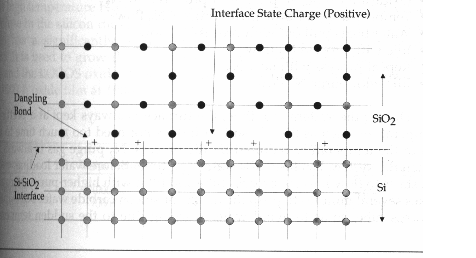
Fig. 5 Dangling bonds induce interface state charge. [3]