Linear and Parabolic Rate Constants
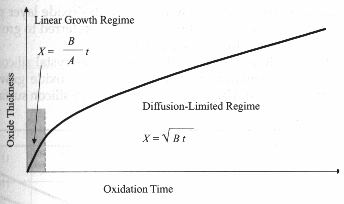
Fig. 3
Illustration of the two oxidation rate regimes. [3]
The equation d02 + Ad0
=B(t+t) has two important limiting
conditions:
1.
One limiting case occurs for long oxidation times and we
get
d02 = Bt
This is called Parabolic Law and B is the parabolic
rate constant. This is
diffusion-controlled case.
2.
For short oxidation times we get
d0 = B(t+t) / A
This is called Linear Law and B/A is called the linear
rate constant and it is a reaction-controlled case. [3] [2]