Operation of
an ion implanter
The main function of the ion
implanter is to deliver a beam of ions of a particular type and energy to the
surface of a silicon wafer. [1]
- A gas source feeds a small quantity of source
gas such as BF3 into the ion source, where energetic electrons emitted
from a hot filament ionize the dopant atoms.
- An extraction voltage, V kilowatts (kV) causes
the charged ions to move out of the ion source into the analyzer.
- The magnetic field of the analyzer is chosen
such that only ions with the desired charge to mass ratio can travel
through without being blocked by the analyzer walls. A magnetic field B is
applied normal to the path of ions with charge q and velocity v. The force
on the ions is given by F=qvB
and the ions move in a circular path of radius r and there is a
centripetal force,†††††††††††††† F=M v2/r.
Therefore,
qvB=Mv2/r [velocity v is
unchanged]
And†††† r
= Mv/qB ------------------------------------(1)
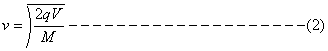
Now for
an ion accelerated through a potential V the velocity is given by:
Mv2/2 = qV , from
where we get v as:
†††† † ![]() ††††
†††† 
†††††††††
††††††††† From
(1) and (2) we get
†††††††††††††††††† 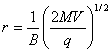
For a
given acceleration potential and magnetic flux density, the radius of the ion
path is directly proportional to the square root of the mass-to-charge ratio.
†††††††††††††††††† 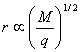
Thus we
get the desired dopant species.††
- Surviving ions, which are the desired dopant
species enter the acceleration tube where they are accelerated to the
implantation energy as they move from high voltage to ground voltage.
∑
The beam is then scanned over the surface of the wafer
using electrostatic deflection plates. The wafer is tilted with respect to the
axis of the acceleration tube so that neutralized ions donít hit the wafer.
∑
The silicon wafers serve as targets for the ion beam and
the complete implanter system is operated under vacuum condition.[2]
††† 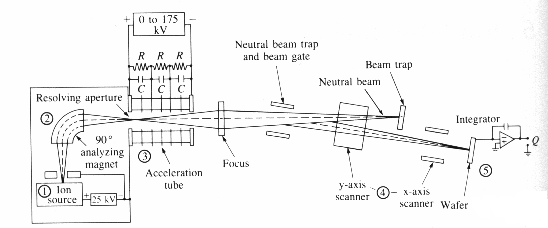
†††††††††††††††††† Fig 1 Schematic drawing of a
typical ion implanter[1]